The horn is one feature of the car that simultaneously saves lives, alerts other drivers, and acts as an emergency feature for ambulances and police cars. Car horns are simple car devices that generate noise by using compressed air. They are generally used to alert the drivers in front of them that they need to overtake or that they are getting closer to the driver’s vehicle.
Car horns are distinctive in that they provide the background sound to numerous cities throughout the world. Car horns are now required on all vehicles, and their use may be subject to additional rules depending on the state you distribute them to.
Here is the complete history, types, and other important details about car horns.
What is a car horn?

A car horn is a sound-producing device that can be installed in vehicles. The sound usually resembles a “honk” in old automobiles and a “beep” in newer vehicles. The horn is used by the driver to alert people of the vehicle’s proximity or the presence or to draw attention to a hazard.
Car horns are used as a signal when locking the car with remote control, in addition to serving as a warning. The softer horn is frequently used by the central locking mechanism. During a break-in, most alarm systems use car horns as both a barrier and a plea for attention.
The electric automobile horns’ record of durability and lifespan is absolutely astounding, given their size and the passionate activity that goes on within. This is maybe why it hasn’t been replaced by a strong electronic audio device.
A standard car horn is made up of a flexible metal diaphragm, an electromagnet wire, a switch, and a casing that operates like a megaphone. The entire device follows Hooke’s Law, which means that if the horn is properly designed, the movable diaphragm will swing back and forth constantly when current is applied. This will result in the sound that a horn produces.
Truck horns

Truck horns are usually attached to fire trucks, semi-trailer trucks, and trains. A truck horn is a device that alerts other motorists and pedestrians on the road that a truck is near. A truck horn is also used to scare wildlife away from the highway. These devices create such a loud sound that they can be used to issue warnings even from quite a distance.
It is a pneumatic device that produces a very loud sound for signaling applications. It usually includes a compressed air source that travels through a diaphragm into a horn. The airstream makes the diaphragm vibrate, creating sound waves, which are subsequently amplified by the horn.
To open the valve, a cord situated on the roof of the driver’s cab is pulled, giving varied volumes of air to the horn in trucks. An extended hand reaching upward and pounding is a request for a toot from the driver of an air horn-equipped truck. The horn is activated via a button on the steering wheel in modern trucks. Some trucks include a switch on the dashboard that allows consumers to choose between an electric and an air horn. This is to prevent the powerful air horn from being used in populous areas.
Truck horns were originally installed on diesel locomotives. The need for a distinctive-sounding railway horn became obvious after an accident in which a vehicle mistaken a train for a truck. As a result, North American trains now contain at least two air horns, each with a different tone, that play simultaneously, generating a harmonic interval or chord. Each horn is referred to as a “chime.” The most popular chime horn combinations are three and five, however two chime horns are also available.
The installation of large air horns on trucks, cars, and bicycles has been fashionable in recent years. Some jurisdictions prohibit the attachment of an airhorn, regardless of whether it may be operated because of the extremely loud sound that they produce.
Motorcycle horns

Motorcycles have horns for the same purpose as other vehicles do: to avert collisions by phonically alerting other drivers on the road.
Motorcycle horns are normally electric horns, powered by a circular steel diaphragm with an electromagnet working in one direction and a spring working in the other. The diaphragm is connected to contact points that periodically stop the current to the electromagnet, forcing the diaphragm to spring back in the opposite direction, completing the circuit once more. This setup opens and shuts the circuit several times per second, producing a loud noise similar to an electric bell, which is then amplified by a horn.
Although using two different frequencies is more perceptible than using two horns of the same frequency, especially in an area with a high noise level, horns are often used in pairs to generate an interval with two notes, sounded together.
Some motor scooters and motorcycles now use a less expensive and compact alternative design that, although keeping the name “horn,” foregoes the real horn ducting in favor of a larger flat diaphragm to achieve the appropriate sound level.
What is a car horn used for?

The function of modern automotive horns has remained the same over time, however, they have become less dependent on electronic magnetic interference and power. A car horn serves as an early warning signal for drivers. The majority of accidents occur when people are unaware that vehicles are approaching from separate or opposite directions. A car horn alerts everyone, whether it’s another car, a pedestrian, or an animal, to avoid any form of accident.
Another typical function of car horns is to alert other cars that the stoplight has changed, particularly if they fail to move quickly enough. While waiting for the traffic light to turn green, drivers frequently check their phones, which prevents them from noticing when the light has changed and it is safe to proceed. Honking on the driver in the front will alert him or her that it is time to leave.
A car horn is also used to honk while backing up the car in the driveway. Honking while reversing alerts individuals close to the vehicle’s movement, alerting them to keep a safe distance. This is particularly significant since it reduces the chance of accidents, which is particularly necessary for little children playing nearby.
Car horn history
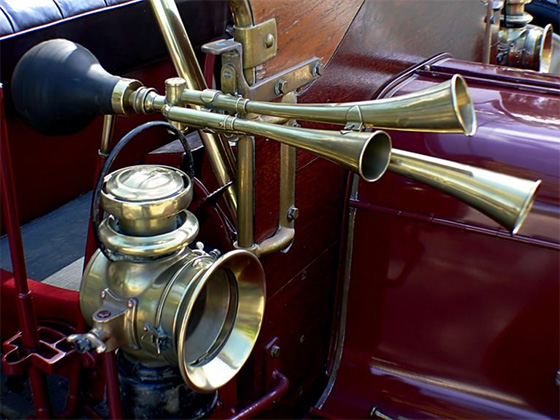

Horns date back to the mid-nineteenth century in Britain, when steam-powered carriages were only becoming popular. Self-propelled vehicles on public highways had to be led by a man on foot waving a red flag and blowing a horn for the safety of pedestrians and animals. Nevertheless, it did not take long to understand that a car-mounted horn was more effective than a horn blown by someone strolling in front of the automobile, which lasted around ten years.
Some individuals desired a more effective warning system, according to Atlantic Lexus in Farmingdale, NY, one that can be heard at least a 1/8th of a mile ahead. The search for effective in-car signaling devices at the turn of the twentieth century irreversibly altered the acoustics of highways. Car owners could choose from a variety of whistles, sirens, and bells to manually alert pedestrians and other drivers on the road.
It was in 1908 when Miller Reese Hutchison, a youthful inventor, patented the Klaxon Horn. Hutchinson, who collaborated with Thomas Edison on the Klaxon Horn, designed two versions. As per MoparMagazine, one version of the horn was battery-powered, while the other was manual and operated by a little hand crank. The Klaxon Horn made a distinctive “aoogha” sound to notify the approach of each vehicle in both versions. If one blows a horn at a pedestrian today, there are annoying looks that follow. Honking to alert pedestrians of the presence of moving vehicles was considered courteous in the early 1900s.
In the 1930s, the Klaxon Horn had lost favor because of the electric horn. Although the “aoogha” of the Klaxon Horn is still iconic, the tone of automotive horns has changed through time. Modern car horns are divided into three categories: compressor trumpets, disk horns, and fanfare horns. Compressor trumpets are commonly found on commercial vehicles. The disc horn and fanfare horn, on the other hand, are designed for personal automobiles. The sound of disc horns is characterized as metallic, while the sound of fanfare horns is characterized as richer and more harmonic.
In the 1960s, one noteworthy horn took a new turn by not using the typical two-tone sound. The Plymouth Road Runner’s horn had a featured high-pitched, single-toned “beep-beep” that resembled its famous cartoon namesake. The sound of the Road Runner didn’t quite match its strong muscle car look, but it was clearly noticeable.
The automobile horn has its origins in road safety, which is just as crucial today as it was back then.
How do car horns work

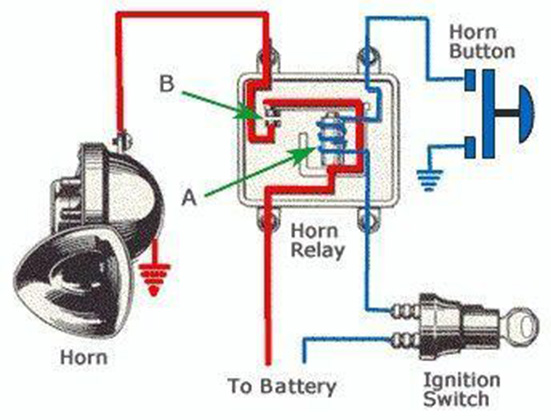
A car horn is a very basic electromechanical device that makes noise by using the concept of electromagnetism. A standard car horn is made up of a flexible metal diaphragm, typically made of spring steel, an electromagnetic coil, a switch, and a casing that operates like a megaphone.
As per Hooke’s Law, the “expansion of a spring is directly proportionate to the load supplied, given the limit of proportionality is not exceeded”, the entire apparatus works. This is a technical way of saying that if the horn is designed correctly, the flexible diaphragm will go back and forth endlessly as long as power is applied. This will result in the sound that a horn makes.
A flexible electrical connection is attached to or triggered by the diaphragm in the construction of horns. The flexible steel diaphragm is coupled with a powerful electromagnet that drives a central armature. When current is given to the electromagnet, the armature reaches its mechanical limit, disconnecting electricity for a brief duration. Electrical contact is made again as it goes back to its starting place, and the armature resumes its travel.
Moving all of this mass to produce a loud, prolonged sound that is frequently in excess of 90 decibels requires a lot of energy, as consumers might expect. Of course, the energy is an electrical current, and the only item in cars with electromechanical horns that requires more is the starter. Headlights, power seats, and other accessories utilize less current than horns. That is why horn wiring and terminals are so enormous, as well as why a relay is required to operate the horns.
When the horn button is pressed, the electrical contact opens, allowing current to flow to the relay, which then supplies high current to the electromagnet of the horn. As a result, the diaphragm is drawn in and flexes to its mechanical limit. The contact is disengaged, and the current flow to the electromagnet is blocked. The diaphragm is allowed to return past neutral before the switch is closed, drawing the diaphragm back and establishing an equal oscillation.
Horns are available in an infinite number of notes or frequencies. The versatility of the diaphragm, its physical size, the strength of the electromagnet, the size of the diaphragm, the mechanical design of the switch contact, and the size and shape of the horn’s casing, and a variety of other parameters all contribute to the horn’s note.
A low-note and a high-note horn are standard on most collector automobiles. The integration of the two sounds is what gives a vehicle its characteristic sound. Remarkably, larger cars always had horns with a lower overall frequency honk, but tiny car horns were bent toward higher frequencies. As a result, Volkswagen’s “beep-beep” and Cadillacs make French-horn-like sounds.
Many countries, believe it or not, mandate car horn manufacturers to set a car’s precise horn frequency. The notion is that a high-pitched horn sound indicates a tiny car, whereas a lower-pitched horn note indicates a larger vehicle.
Different types of car horns
There are about seven different types of car horns available today that are explained in detail below.
Air car horns

An air horn is a device that makes a very loud noise by compressing air. Air horns are used by big cars, emergency vehicles, trains, and ships to warn other drivers of their presence.
Air horns are those that use air pressure to operate. When the air inside the horn compresses and passes through a reed, a sound is produced. Air pressure horns are typically found in vehicles with air tanks. The air pressure brake system can then be used that way. When there is extra air that may be used to pressure, air pressure horns are particularly effective.
A basic air horn consists of a compressed air chamber connected to a valve that permits air to flow into a resonating horn. Because air horns work on the same concept as brass instruments, you might think of them as beefed-up brass instruments. An air car horn, like a trumpet, can be tuned to produce specific sounds or tones. People can tell not just that something enormous is approaching, but also what vehicle is approaching by listening to different air horn sounds.
Electric car horns
Electric car horns are common in modern vehicles such as personal automobiles. It is divided into two types: wind tone and electric horn type. For audio and brake systems to work, both need the electromagnetic principle.
The difference between the two types of electric horns is in the way the sounds are produced. The horn emanates directly from the diaphragm and then to a windpipe in the wind tone type. It’s prevalent in cars today since it acts as a bugle to open the door.
Vehicles with electric horns provide warning signals produced by an electrical circuit. To generate the fundamental frequency and force the diaphragm to vibrate, a coil is magnetized and demagnetized. This creates a lot of pressure inside the electric horn, which produces a sound. Electric horns have a significant advantage over other horns in terms of wear resistance, resulting in 10 times longer average lifetimes.
Electric horns are also available in a variety of decibel and pitch levels. The size of the vibrating disc, the stiffness of the spring, and the distance the disc moves determine the pitch levels of these horns. A high-pitched sound is produced by a single horn, such as those seen on tiny cars.
The electronic horns are also installed in emergency vehicles to generate a sound that is immediately identifiable.They’re usually part of the same system as the vehicle’s siren and play through the same speakers. Electronic audio systems with more widely changing frequencies have been popular as auxiliary warning systems in recent decades.
Snail horns

Snail horns are spiral shaped, just like a snail, hence the name. To better fit the acoustical susceptibility of the diaphragm with open air and more effectively transfer sound energy, a spiral exponential horn (often termed the “snail” horn) is cast into the core of the horn.
Ship horns

Ships stray out in the seas all the time, with no other means of communication beyond horns and lights. The fact is that every ship has an air horn that runs on compressed air from the powerplant steam.
It permits the production of a thin sound or whistle, which is perfect for use at sea. Because ships have far-flung targets, these noises have a lower frequency. It’s a means of announcing the ship’s coming from afar.
Ships use air horns, sometimes known as whistles, to communicate with one another and the shore, which are powered by compressed air or steam drawn from the power plant. Low frequencies are employed because they travel farther than higher frequencies. Ship horns can be heard up to ten miles away. Generally, the larger the ship, the lower the frequency of the horn will be.
The RMS Queen Mary, a steamship launched in 1934, had 3 horns tuned to 55 Hz, a frequency chosen because the extremely loud sound would not be uncomfortable to passengers. Ships over 660 ft in length must have horn frequencies in the range of 70–200 Hz, according to modern International Maritime Organization rules.The range for vessels between 660 and 250 feet is 130–350 Hz , and for vessels under 250 ft is 70–700 Hz.
Klaxon car horn

Maybe you’ve never heard of the Klaxon horn. Since it is employed exclusively as a hallmark of electromechanical bran, it is one of the most unusual sorts of horns. Klaxon is similar to the devices seen in trains, ships, and automobiles. Klaxon horn makes sounds like “kalooga” or “ahooga”. The intriguing aspect is that it comes from the Greek term “klaz,” which literally translates to “I shriek.”
Bulb car horns

A bulb horn is a cone-shaped air device used for signaling in cars, bicycles, buses, and other vehicles. A bulb horn operates on the concept of multiple sound reflections.
Bulb horns are often constructed from rubber in the shape of a bulb. It’s a tube with a conical opening on one end. Bulb horns are connected to a metal horn that is activated when squeezed. In the beginning, the airwaves come out, and the horn makes a sound. The idea for bulb horns comes from sound reflection. It’s usually seen on bicycles. It has also been upgraded technologically and is now seen in commercial vehicles.
Waterproof car horns

As the name suggests, waterproof car horns are designed to repel water and don’t get damaged by rainwater or normal car wash. These horns are best suited for areas that are prone to a lot of rainfall, However, waterproof car horns are ideal for all vehicles for added safety.
Conclusion
Since automobiles are continually evolving in today’s world, it is vital to change their components, including horns. After all, the horn is an important indicator and guidance for both drivers and pedestrians. You should be completely aware of the importance of car horns now that you are acquainted with the numerous types.
Sunway, an auto parts manufacturer, provides car horns that offer a more sophisticated and novel way of employing them. Their horns have been designed to use less energy while still extending their longevity.








